
The emergence of Web 2.0 means that people have officially entered a “new media era.” TikTok has successfully emerged from the short-form video platform with a series of precise and targeted strategies that quickly took the world by storm and brought considerable dividends to the company. However, with the irregularity of the short video market, the Tiktok platform has also suffered from short-form video shortcomings, lack of regulation, and addiction issues. This article will look at the background of its birth, the reasons for its success, the business model behind its platform, and finally, the three types of problems it faces.

The birth of TikTok and the development
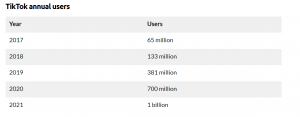
“Helping the public to express themselves and record the good life is the reason for the existence of the video.” (Mancini and Hallin, 2012, as cited in Yang et al., 2019, p . 341). In September 2016, TikTok platforms as a music-based social product by ByteDance with the slogan “Make your day.” On top of providing users with a wide variety of music styles, users are encouraged to shoot videos and complete their work with editing and special effects. Unlike other short video platforms, TikTok’s strategy of focusing on post-95s young people in the first and second tier of inner-city China and incorporating 15s of creative short music videos is spreading rapidly within the Chinese short video market.(Stokel-Walker, 2021. pp.67-68)After continuous product optimization and vigorous promotion, reputation has successfully spread. The number of TikTok users has exploded, starting with the launch of the international version of Tiktok in 2017, rapidly sweeping the world in the short video market. With 850 million downloads and an estimated $1.9 billion in annual revenue until 2020, Tiktok is expected to exceed 1 billion monthly active users by the end of 2021, officially making it the most popular app in the app store. (Iqbal,2021)
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Why it’s successful?
1. Algorithms and technology
The TikTok platform’s algorithm is based on decentralization and high interactivity to precisely target its audience. In the age of new media, people’s access to media has successfully shifted from “passive acceptance” to “active control.” “Audiences are motivated to engage with and use media, and in the process receive some satisfaction from a specific need.” (Whiting&Williams,2013,p.363). Based on this background, the TikTok platform depends on intelligent algorithms to enable high-quality content to be accurately pushed to its demand audience. In addition, TikTok platforms are changing the traditional community media rule, which determines the exposure of short videos based on the number of followers and mainly pushing original content creation. So that each user-produced short video content has an equal chance of exposure, prompting more ordinary short video producers to have enough confidence and motivation to produce original videos, thus achieving the character of decentralized.
On the other hand, from the perspective of content creation, the TikTok platform has introduced many creative ways to express content through combining music, AI effects, and filters, driving more users to participate in the production and dissemination of creative content actively. This has helped bring the producers and users closer, forming a complete marketing chain from the original video to the secondary distribution and the full spread. Carlie D’Amelio’s who create remote dancing, is a perfect example.
It will help you learn the relationship between creators and participants and TikTok Platforms.
- Content diversity and localized features
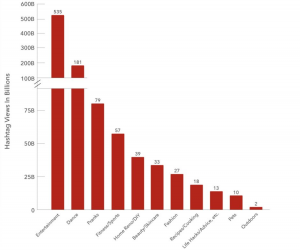
Along with the rapid growth in the number of users on the TikTok platform, its content has gradually shifted to a more diverse and mainstream direction, making every effort to form a relatively diverse and rich content ecosystem to meet users’ diverse choices content quality. Currently, the platform covers 20 categories of content such as fitness, food, and beauty, with 535billion as the main entertainment content category (MediaKix,2020). At the same time, with the continuous development of Internet technology, the process of global integration has accelerated. The communication of globalized and multicultural in timely is valued, but TikTok still pushes localized content according to an algorithmic formula. As Zhang Yiming, founder and CEO of ByteTok, thoughts, the formula for internationalization is to present global products and localize content. (Ma, Hu, 2021, p. 385) This, therefore, allows TikTok to penetrate all aspects of social life in all directions, with the ability to lead in different areas and directions. While strengthening the brand reach and distribution of TikTok’s short videos, the new users who join are no longer limited to the target group that TikTok initially set out to reach.
The category of TikTok

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
With the successful development of arithmetic based on the TikTok platform, the core of its business value is more apparent – traffic.
Business Model
The principal value of TikTok is its large user base (Travis, 2020), and advertising is one of the most obvious ways for TikTok to converts traffic to profit. In June 2020, TikTok launched an app called “TikTok for Business” as a way for brands to place their ads, which can be broadly divided into three categories, including in-feeds ad, branded acquisitions, and branded hashtag challenges. As an example, up, a digital banking app that wanted to launch a new brand platform called Easy Money, ran ads on TikTok for both the branded hashtag challenge #UpEasyMoney and TopView and partnered with critical creators who had a following in order to attract a broad audience and increase engagement. As a result, the brand quickly garnered over 25 million views and generated over 250 pieces of relevant user-generated content, increasing ad recall by 7.6% and brand preference by 29%(“TikTok For Business Case Study: Up”, 2021).This cycle of content supporting traffic, turning into capital, and capital feeding content creates a win-win situation for TikTok and the creator. In addition, is TikTok coins, in which users reward their favorite creators with virtual currency purchased with real money, of which TikTok would take a percentage interest, then the creators could convert the remaining virtual currency into real money (TRAVIS, 2020).
#UPEASYMONEY hashtag challenges


This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Disadvantage
- Limitations and homogenization
TikTok’s platform has single and fragmented information content, making it hard to meet the satisfaction of complex, in-depth advertising content to brands, reducing their profitability. Secondly, the repetitive use of short videos has led to the homogenization of TikTok videos, which is likely to cause aesthetic fatigue and is not conducive to the sustainable development of the platform. (Yang et al., 2019, p . 341)
- internet addiction and attention degradation
TikTok’s intelligent algorithm calibrates interest content based on the user’s data, leading to addiction (Marinescu, 2019). Once humans become accustomed to this fast-paced, fragmented, and shallow information age, it will lead to the degradation of their attention span and the gradual loss of their ability to think logically, creating an “entertainment to death The spread of the social phenomenon of “entertainment to death,” whereby humans willingly become subservient to entertainment.
- Inadequate control of harmful content
In today’s highly polarised political environment, fragmented media constructs alternative realities for its readers and viewers (Lee Bouygues, 2021). Some unscrupulous creators use TikTok videos as a medium for piecing together fake news propaganda to mislead viewers; some users use offensive performances to attract followers. The current market regulators have not yet been able to control this emerging short video platform precisely, and the existing legal provisions and administrative regulations are challenging to regulate the short-form industry in a comprehensive and detailed manner.
Conclusion
TikTok is a “decentralized” vegetarian original content production method that provides entertainment and learning content for young people in their fragmented time. However, as TikTok is still in its early stages of development, there are still shortcomings such as lax regulation, poor online culture, and too much-homogenized content. TikTok needs to integrate deeply with various fields, form a distinctive application model, and cultivate a more distinctive online culture and value orientation to become an irreplaceable short video Platform from the competition of various products.
【word count:1293】
References:
Stokel-Walker, C. (2021). TikTok Boom : China’s Dynamite App and the Superpower Race for Social Media. Canbury Press.
Iqbal, M. (2021). TikTok Revenue and Usage Statistics (2021). Business of Apps. Retrieved 17 October 2021, from https://www.businessofapps.com/data/tik-tok-statistics/#1.
Ma, Y., & Hu, Y. (2021). Business Model Innovation and Experimentation in Transforming Economies: ByteDance and TikTok. Management and Organization Review, 17(2), 382-388. doi:10.1017/mor.2020.69
TikTok For Business Case Study: Up. TikTok For Business. (2021). Retrieved 17 October 2021, from https://www.tiktok.com/business/en/inspiration/up-315.
Yang, S., Zhao, Y.L., & Ma, Y. (2019). “Analysis of the Reasons and Development of Short Video Application——Taking Tik Tok as an Example.”2019 9th International Conference on Information and Social Science(pp.340-343).) Francis Academic Press,UK.DOI: 10.25236/iciss.2019.062
The Most Popular TikTok Hashtags By Categories & Topics [Examples]. Mediakix. (2021). Retrieved 17 October 2021, from https://mediakix.com/blog/most-popular-tiktok-hashtags-categories-topics/.
Marinescu, A. (2021). Teens Addicted to TikTok. Taft Tribune. Retrieved 17 October 2021, from https://tafttribune.org/4290/opinion/teens-addicted-to-tiktok/.
MSNBC. (2020, January 7). Julián Castro endorses Elizabeth Warren [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uk2Tzc8H5po
Inside Edition. (2020,March 31).How Charlie D’Amelio’s#DistanceDance Is Fighting COVID-19[Video]YouTube.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fS6913bBVek
Whiting, A., & Williams, D. (2013). Why people use social media: a uses and gratifications approach. Qualitative Market Research, 16(4), 362–369. https://doi.org/10.1108/QMR-06-2013-0041
<a rel=”license” href=”http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/”><img alt=”Creative Commons License” style=”border-width:0″ src=”https://i.creativecommons.org/l/by/4.0/80×15.png” /></a><br />This work is licensed under a <a rel=”license” href=”http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/”>Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License</a>.



