
Platform Businesses
Throughout the years there has been a rise in technological innovations and increased online connectivity (Deloitte The Netherlands, 2018) which has allowed for the role of digital labour market matching to increase thus contributing to the rise of the platform economy (Deloitte The Netherlands, 2018). These platforms now have a big influence in shaping social life as they have now gained a gigantic scale and level of use (Van Dijck, Poell & de Waal, 2018), and convey the idea of platforms not as a single application but as ecosystems as they bring together interaction users, corporate entities and public bodies (Van Dijck, Poell & de Waal, 2018).
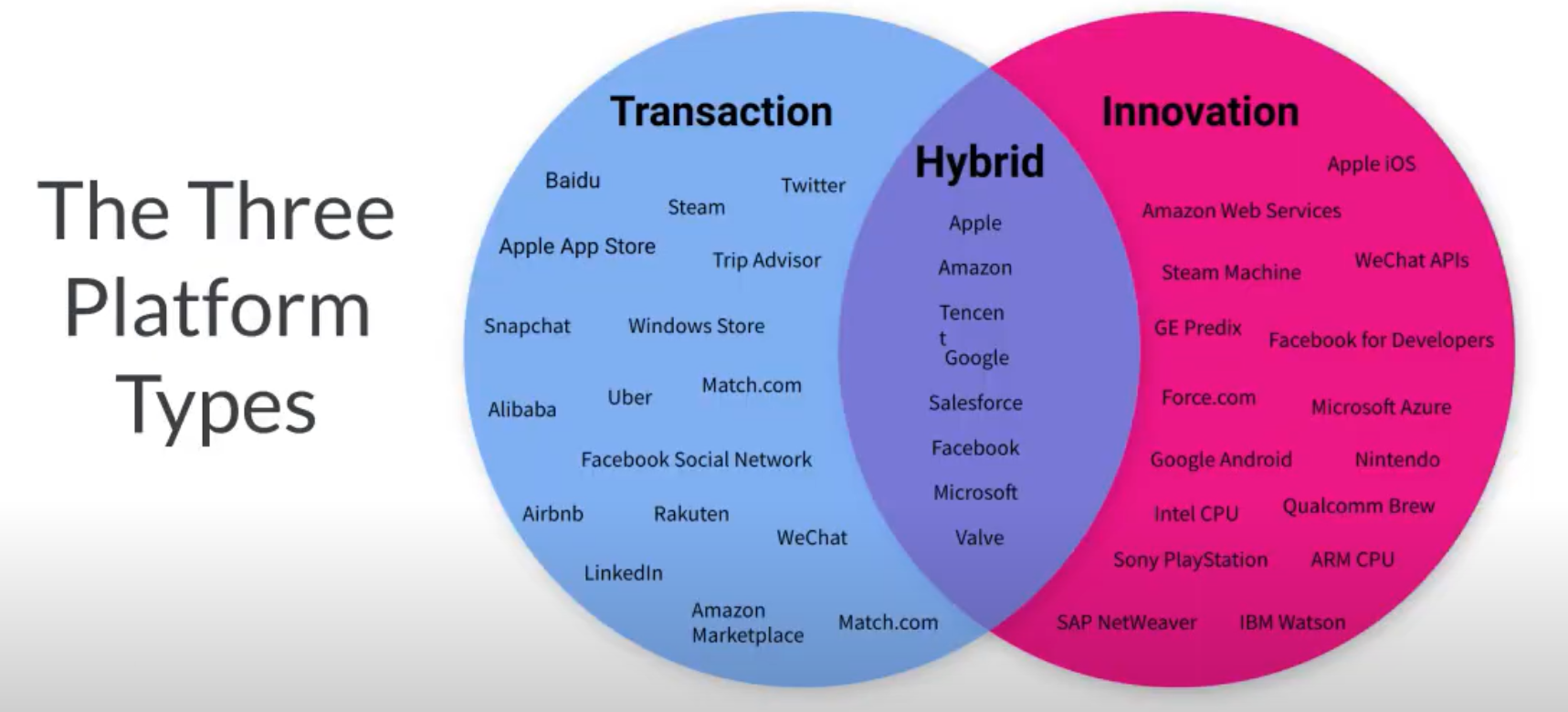
(Figure 1: image of the three platform types)
This image provides more understanding of what digital platforms are and goes through 3 kinds of digital platforms which are:
- Transaction
- Hybrid
- Innovation
The term digital platform can be seen as ‘any type of digital platform that uses the internet to connect dispersed networks of individuals to facilitate digital interactions between people’ (Deloitte The Netherlands, 2018). These platforms do not own the means of production but instead they create the means of connection (Deloitte The Netherlands, 2018), the strength of the platform economy is seen by how much it can eliminate trade barriers by using information and the circulation of data for its own advantage (Deloitte The Netherlands, 2018). Therefore, providing an open economic system which allows for much greater participation of its users.
Consequently, many platforms also use the ‘free’ strategy which has developed an ecosystem in which the default mode is to trade convenient services for personal information (Schneier, 2015, as cited in Van, 2018). So, by accumulating users information and data in a more exact and speedy way allows the platforms to target and profile specific users and user groups, ultimately performing it’s own demographic profiling and consumer targeting (Van, 2018).
Therefore, in this essay we will be looking at Facebook as a case study to demonstrate the successes and concerns of a platform business, how they operate and how much money they are able to make.
When did Facebook Commence?
Facebook was developed in 2004 and has become the largest social network in the world. This can be seen in the graph below which portrays the world’s most used social platforms with the data showing that Facebook now attracts almost 2.8 billion monthly active users, which is 57 million more than it attracted just three months ago from April 2021 (Kemp, 2021). Facebook has changed the world and has become one of the main platforms for many different media aspects, such as posting, sharing content, sending messages and staying connected with friends and family. One of the main factors as to why it is the largest social network in the world is the idea that users have to be transparent about who they are (Hall, 2021), with Zuckerberg arguing that transparency is required in order to form personal relationships, share ideas and information and build up society as a whole (Hall, 2021). 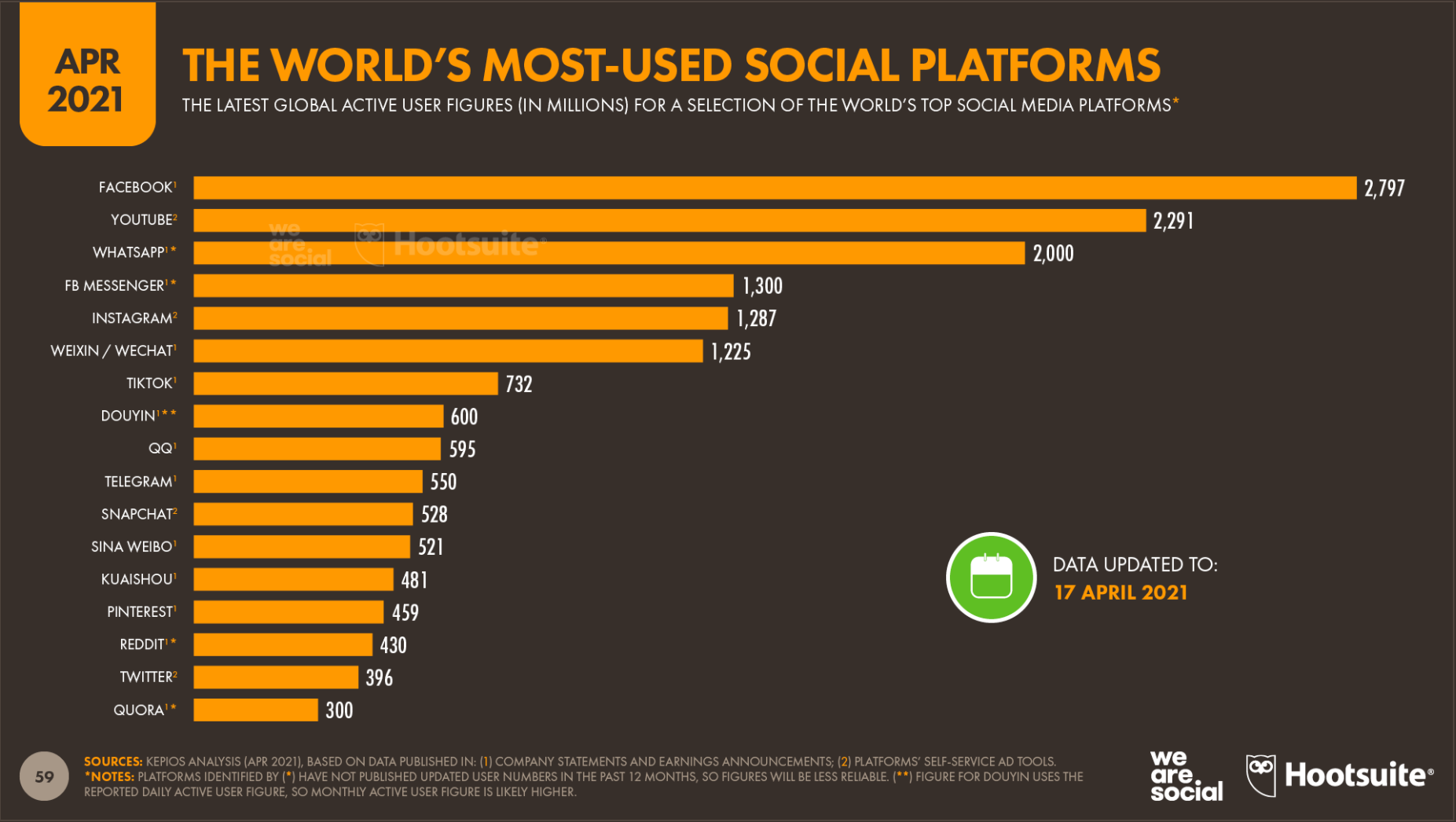
(Figure 2: image of the world’s most-used social platforms)
History of Facebook
The video below is helpful to a better understanding about Facebook.
(Figure 3: video on the history of facebook)
Created by college students at the time (Mark Zuckerberg, Eduardo Saverin, Distin Moskovitz and Chris Hughes) the platform started off as ‘Facemash’ which was a designed to judge the attractiveness of their fellow students but was shut down after two days however gained a lot of popularity and thus adjustments were made and Facebook was then created. It’s popularity quickly increased and by the year 2006 anyone over the age of 13 with an email address could join and ever since it has continued to evolve and grow.
Facebook’s Primary fields of operation and its success:

(Figure 4: image of Zuckerberg’s 10 year road map)
Facebook controls 80% of the market for social networking services, which can be further seen as it has reached over two billion monthly users worldwide (Van Dijck, Poell & de Waal, 2018). They obtained Instagram in 2012 and WhatsApp in 2014 (which can be seen in the image above), thus adding to its success by broadening its original demographic as they added platforms with more appealing visual and messaging features (Van Dijck, Poell & de Waal, 2018). Consequently, through these popular Facebook family mobile apps (Facebook, Messenger, Instagram and Whatsapp), Facebook has been able to gain a significant amount of control over people’s personal information streams. To add onto this Facebook and Google also control more than 60% of online advertising and control a significant share of online identification services which are an important piece of information to many other services.
Therefore, through the years since Facebook was created, it has evolved and transitioned from being just a social network to a cross-platform and now becoming a digital ecosystem and a family of stand-alone apps which all revolve around your digital identity (Hernaes, 2016). Because of this, that is how Facebook’s ecosystem seems to have a competitive advantage against its competitors like Apple, Amazon and Google (Hernaes, 2016). Facebook’s position cannot be challenged as long as it maintains the personal and social digital identity of users in a user-friendly way, as the switching cost is too high. This means that as long as Facebook the whole platform evolves, so does each of its products in the ecosystem (Hernaes, 2016). There has also been a growth in Facebook’s messenger platform with APIs that enable developers to create their own more complex chat bots (Hernaes, 2016) which allow for conversational shopping through the platform, thus combining Facebook pay and the messenger platform show the evolution of Facebook and how it is not only a digital ecosystem of different applications but a digital ecosystem with their own API’s and third party connections (Hernaes, 2016).
To show even more evidence of a growing and developing ecosystem, Zuckerberg has provided us with a ten-year roadmap which can be seen in the image above, thus conveying how the evolution of Facebook is only just beginning and through it’s high ambitions it will continue to evolve and develop even more throughout the years.
How does Facebook make money?
When it comes to Facebook’s business model and how it makes money, users are not paying Facebook anything, at least not directly. How they are able to make money is predominantly through ads within Facebook and Instagram apps with advertising representing 98% of Facebook’s 86bn revenue in 2020 (Franek, 2021). This is also explained very clearly in the video below by Mark Zuckerberg.
(Figure 5: Video about senator asking how facebook remains free)
Therefore, Facebook’s business model offers its services mostly for free for the users and then makes money by allowing businesses to pay for advertising on their services, meaning that the real customers that Facebook focuses on are the small businesses that want to advertise on their apps (Franek, 2021). That being said, there are still a lot of concerns that have been raised about this company, as this business model does have it’s own issues, which is part of the reason as to why Facebook’s success is tainted by so many privacy and security breaches (Franek, 2021).
It has been seen that Facebook’s past privacy and security issues were not one-off accidents but a decade-long pattern of behaviour (Fowler, 2021) in which Facebook doesn’t seem to show any improvement for the security of people’s information. Which is a concern, as ‘without meaningful competition, Facebook has been able to provide lower levels of service quality on privacy and data protection that it would provide in a competitive market’ (Fowler, 2021).
Therefore, putting it all together, even though there are many concerns and downfalls surrounding Facebook, at the end of the day Facebook is still successful and it’s users continue to use it. This is due to the fact that no other online services come close to being compared to Facebook and Instagrams ability to connect users with people they know (Fowler, 2021).
Referencing:
- Deloitte The Netherlands. (2018). The Rise of the Platform Economy Report – Deloitte. Retrieved from https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/nl/Documents/humancapital/deloitte-nl-hc-the-rise-of-the-platform-economy-report.pdf
- Fowler, G. (2021). Perspective | There’s no escape from Facebook, even if you don’t use it. Retrieved from https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2021/08/29/facebook-privacy-monopoly/
- Franek, K. (2021). How Facebook Makes Money: Business Model Explained. Retrieved from https://www.kamilfranek.com/how-facebook-makes-money-business-model-explained/
- Hall, M. (2021). Facebook. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/Facebook
- Hernaes, C. (2016). The evolution of Facebook. Retrieved from https://hernaes.com/2016/04/13/the-evolution-of-facebook/
- History of Facebook. (2018). Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U3RvX42zeis
- Kemp, S. (2021). Digital 2021 April Statshot Report – DataReportal – Global Digital Insights. Retrieved from https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2021-april-global-statshot
- Senator Asks How Facebook Remains Free, Mark Zuckerberg Smirks: ‘We Run Ads’ | NBC News. (2018). Retrieved from https://youtu.be/n2H8wx1aBiQ
- Van Dijck, J., Poell, T. & de Waal, M. (2018). The Platform Society. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 5-32 (‘The Platform Society as a Contested Concept’).
- Van, J. (2018). The Platform Society as a Contested Concept. Oxford Scholarship Online. doi:10.1093/oso/9780190889760.003.0002
- What is a Digital Platform? (2021). Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1aVBp1dFG2Q
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.